All characters, companies, and events in this scenario are entirely fictional. The goal of the scenario is to demonstrate how an owner might use the Paramount Decisions process to select a contractor for a Lean IPD project.
A forward thinking owner is starting a Lean project using Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) and Target Value Delivery (TVD). Due to the high risk of deliverying large-scale projects, the owner hopes that Lean Construction can reduce the likelihood of the project cost and schedule overrun. As a first step, he is selecting a prime contractor to lead the effort during the preconstruction phase.

The first step is to define the decision's goals and objectives. In this situation the goal is to choose a prime contractor for a Lean IPD project. Three highly qualified contractors have passed the owner's pre-selection requirements and have been shortlisted for this project. The owner is using Paramount Decisions to better understand the advantages of the contractors and to make a more informed and transparent selection decision. They understand that the "lowest responsible and responsive bidder" is often not the "best" contractor for the project. Furthermore, there are many qualities of a good Lean contractor that are important for project success but difficult to quantify without a system like Paramount Decisions.
There are three alternatives for this decision: 1) Company A, 2) Company B, and 3) Company C.
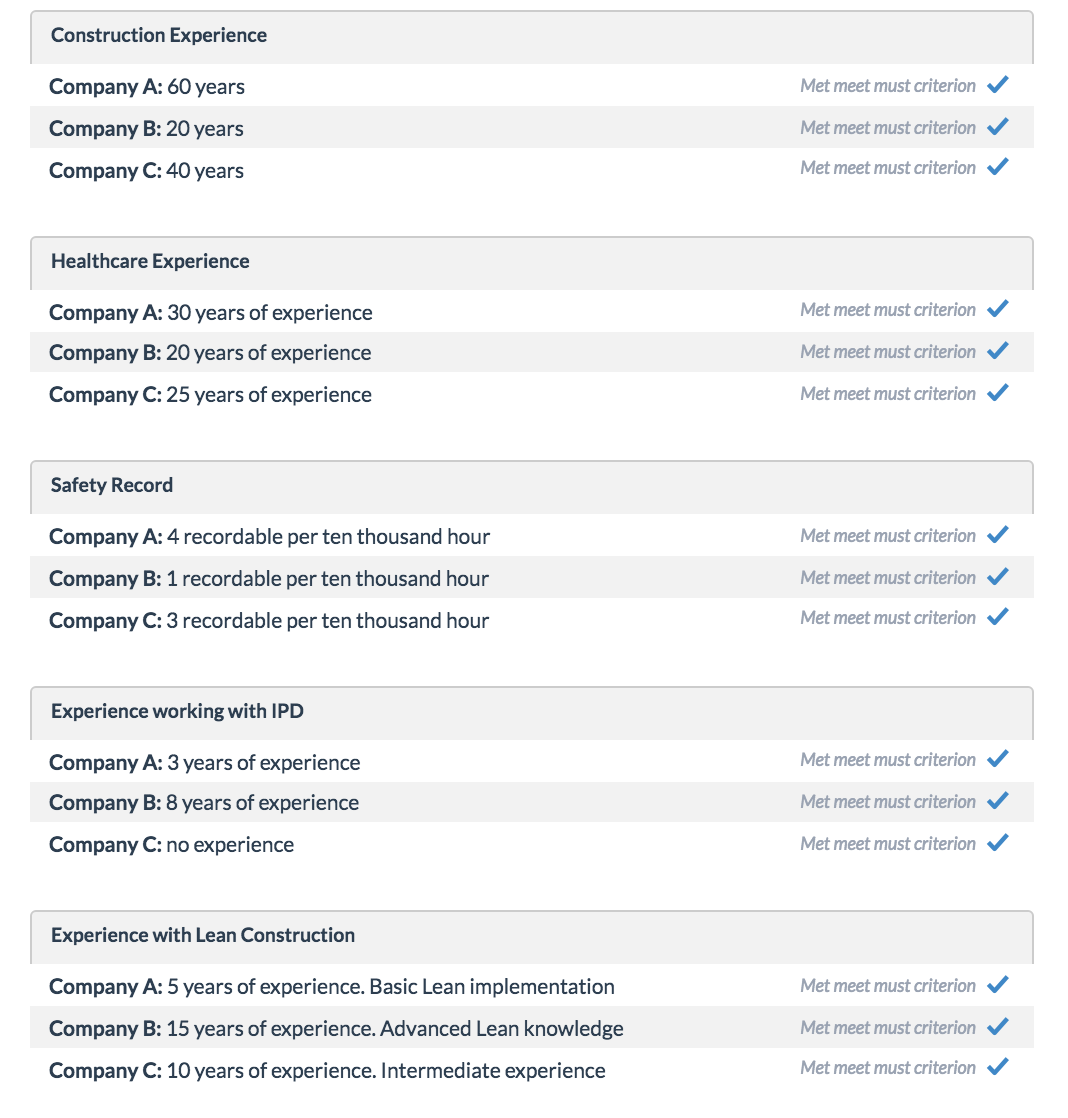
Company A has been in business for over 60 years and has 30 years of healthcare experience. They have been using Lean Construction methods for about 5 years and have 3 years of IPD experience. Company B is a relatively new company with just 20 years of experience. In their short history, Company B has expanded rapidly and is now one of the market leaders in this segment. Company B has been practicing Lean for 15 years and has 8 years of experience with IPD. Company C has been in business for over 40 years with the last 25 years specialized in healthcare construction. Company C has no experience with IPD; however, they have an intermediate knowledge of Lean Construction through 10 years of implementation on Design-Build projects.
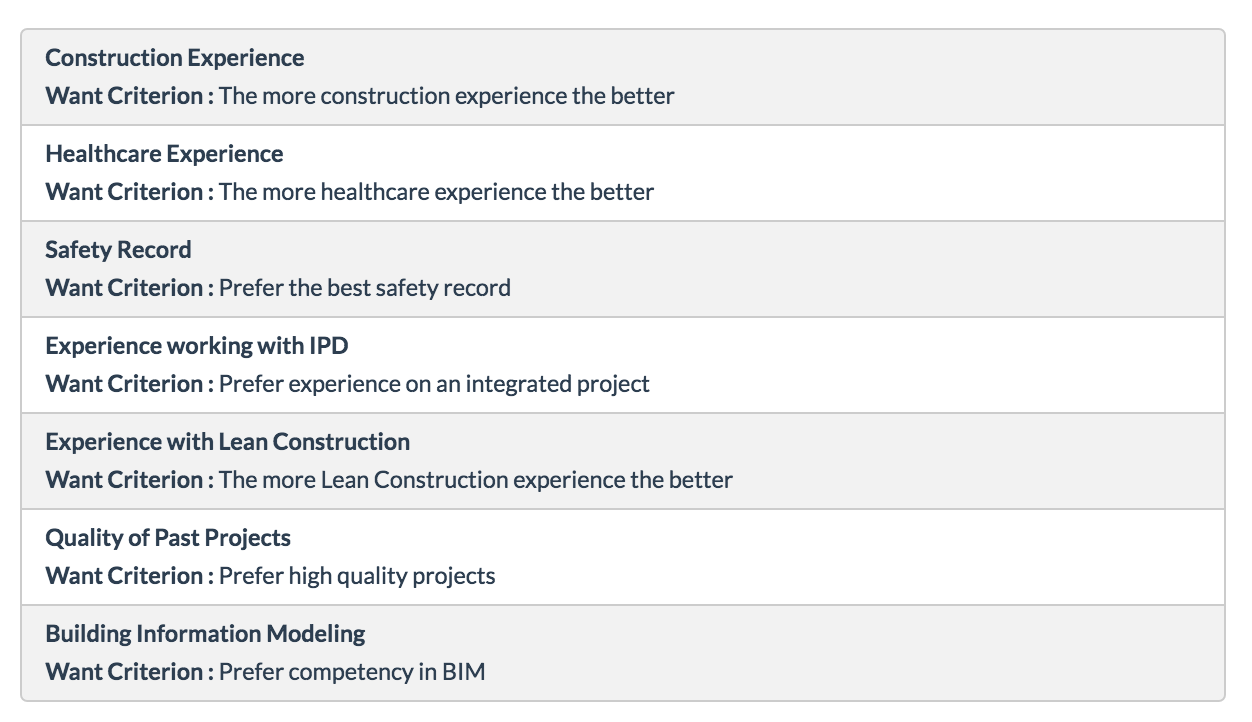
For this decision, the owner has decided to consider the following factors:
1) Construction Experience
2) Healthcare Experience
3) Safety Record
4) Experience with IPD
5) Experience with Lean Construction
6) Quality of Past Projects
7) Building Information Modeling Capabilities
The criterion states how the contractors will be evaluated for each factor and is shown below.
The owner interviews the three company's representative and gather data from projects that have been completed within the last 3 years. The data from projects within the last 3 years are used to evaluate the contractors on their safety record, quality of past projects, experience with Lean, and BIM capabilities.
The attributes of this decision are shown below.
The key insight in making good decisions is to base them on the advantages of alternatives. To determine the advantages, the owner first selects the least preferred attribute within each factor. He then states the advantage of the other attributes relative to the least preferred attribute. Finally, he selects the most important advantage within each factor.
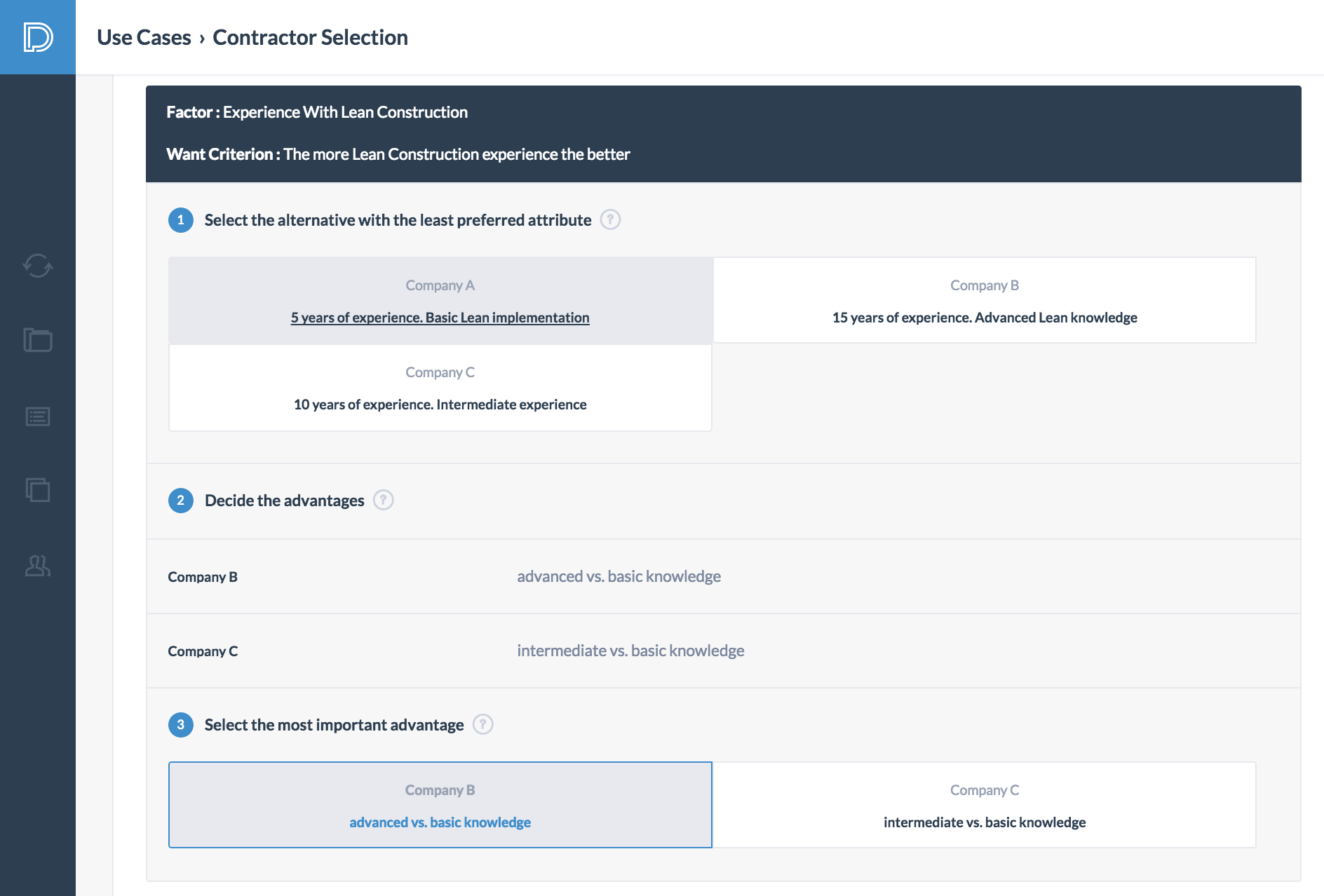
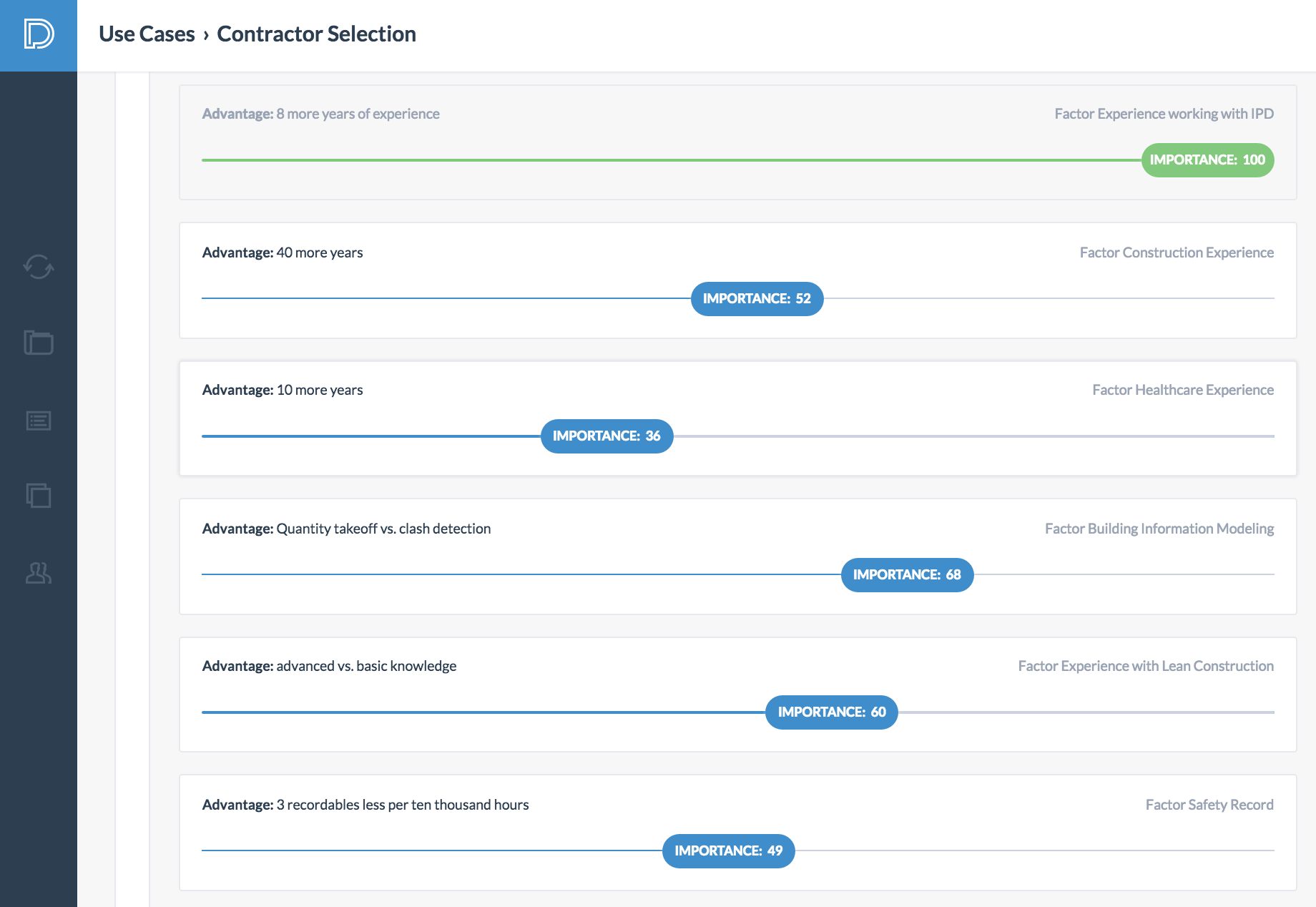
In the sixth step, the owner weighs the advantages. He first determined that the advantage of "having 8 more years of IPD experience" is the most important advantage. This advantage is the Paramount Advantage and receives a weight of 100. The owner then weighs the remaining advantages using the weight of the Paramount Advantage as an anchor.
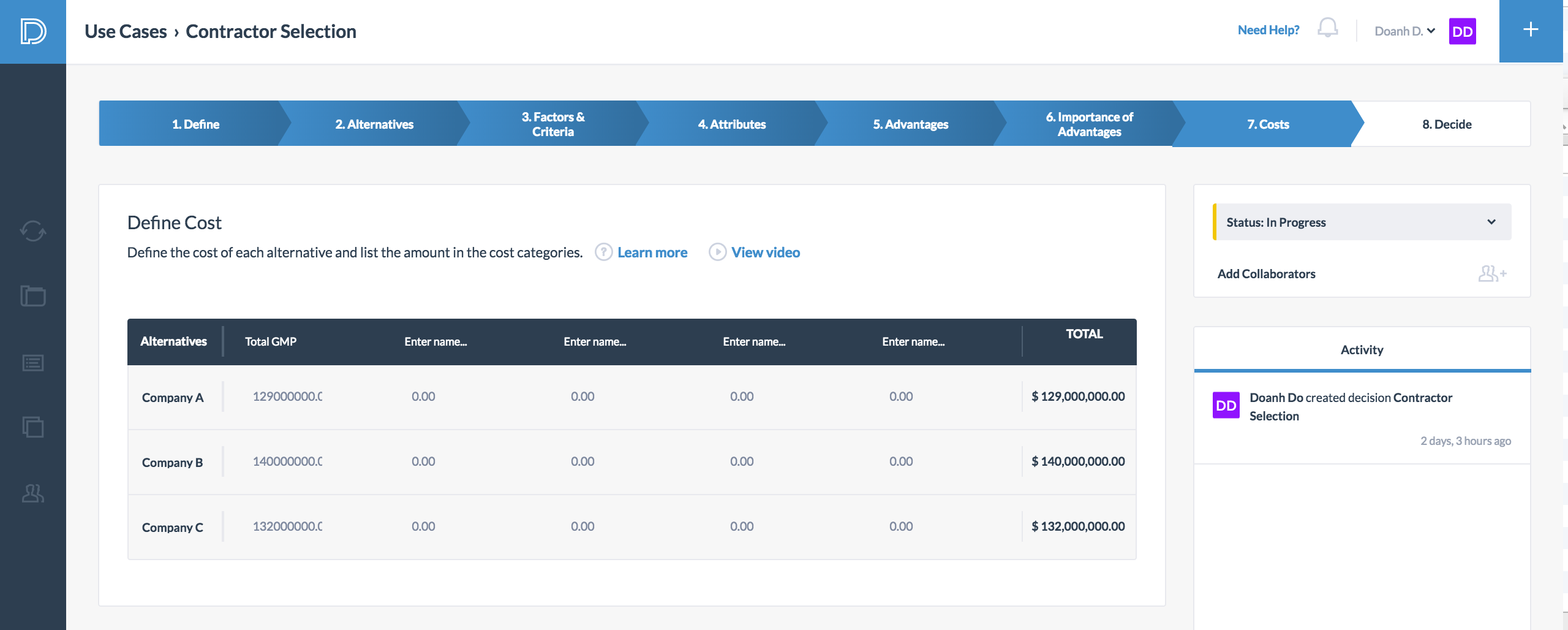
The seventh step in the decision-making process is to define the cost. The total cost includes: 1) the total estimated cost of the project and 2) the contractor's fee. The estimated guarantee maximum price (GMP) for each contractor is shown below.
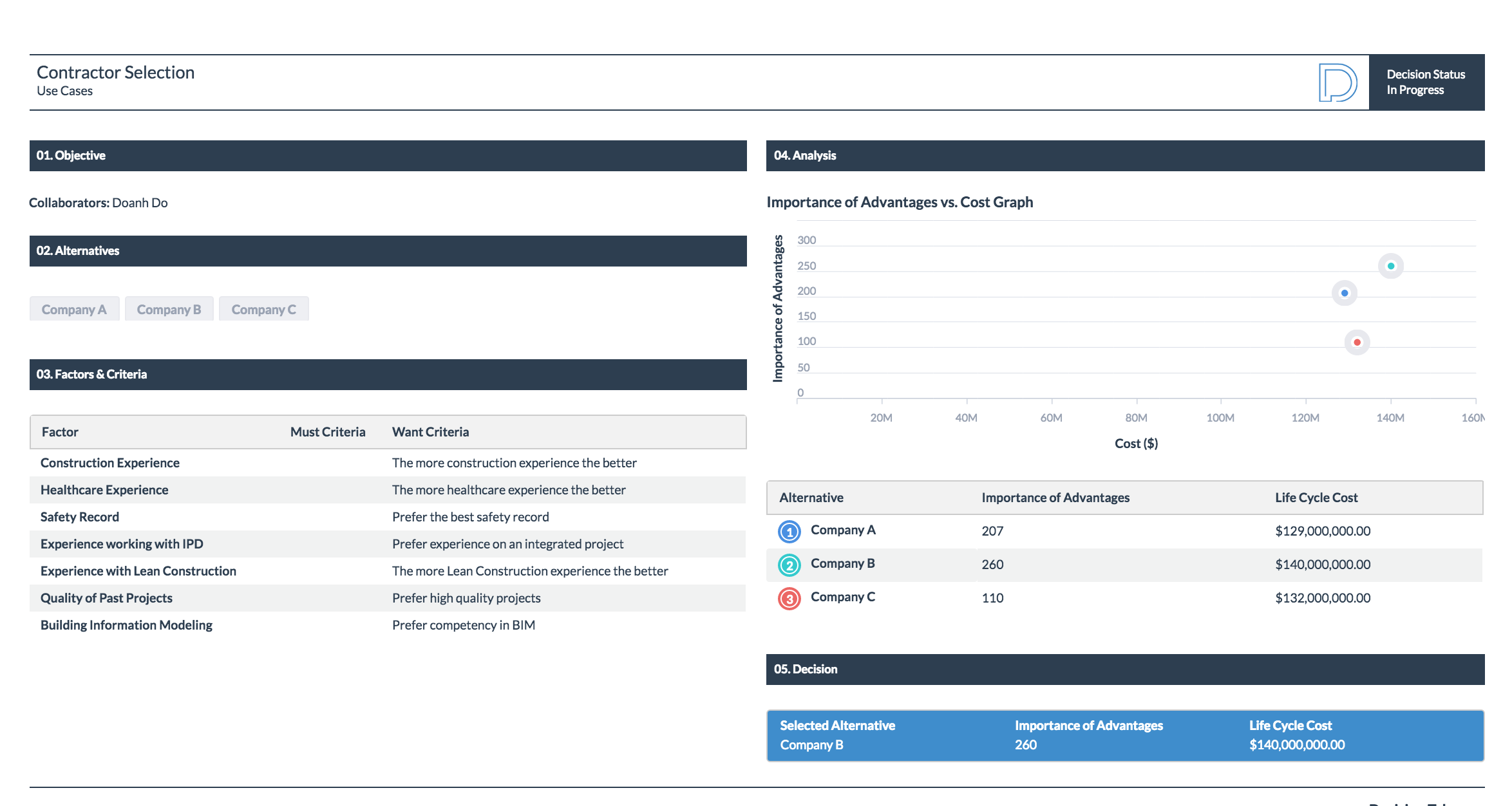
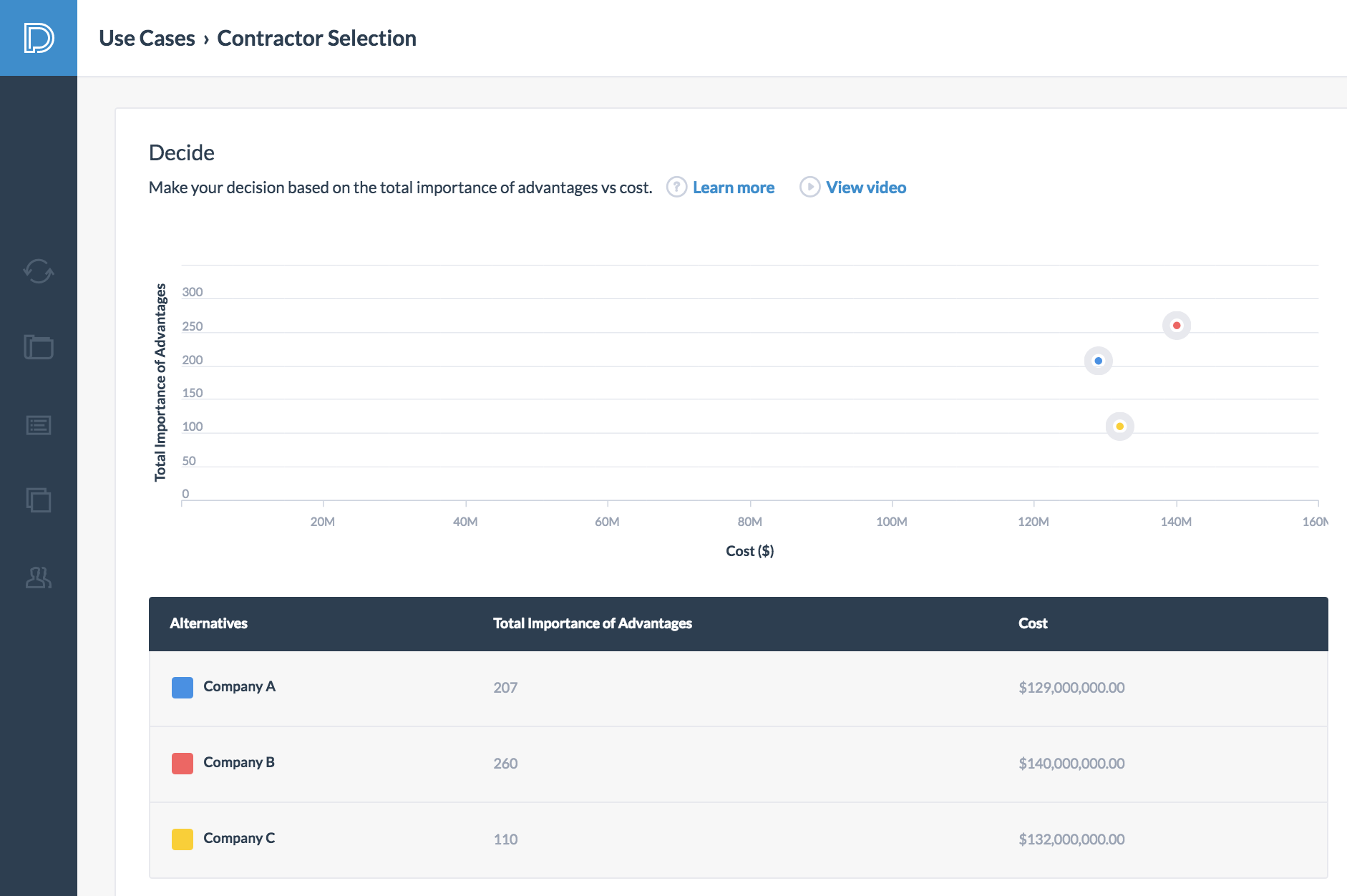
The owner ultimately needs to make his decision base on the total importance of advantages vs cost. In this situation, Company A has a total importance of advantages of 207 and costs 129 million USD. Company B has a total importance of advantages of 260 and costs 140 million USD. Company C has a total importance of advantages of 110 and costs 132 million USD.
For this decision, it is clear that Company C should not be considered because he cost more than Company A while providing fewer total advantages than Company A. The owner needs to determine whether he wants to spend 11 million USD more in order to obtain 53 additional importance of advantages. After some deliberation and a board meeting, the owner decides to hire Company B. Although Company B is the most "expensive" alternative, the total advantages that they bring to the table made them the "best value" choice.
One of the benefits of using Paramount Decisions is the automatically generated reports. The software can create two types of reports base on the data inputted for the decision: 1) a full report and 2) a single page (A3 report). The owner is able to transparently make his decision and communicate the rationale with the companies that were part of the selection process. The owner uses the same factors and criteria to evaluate other selection decision and improves on the template over time.